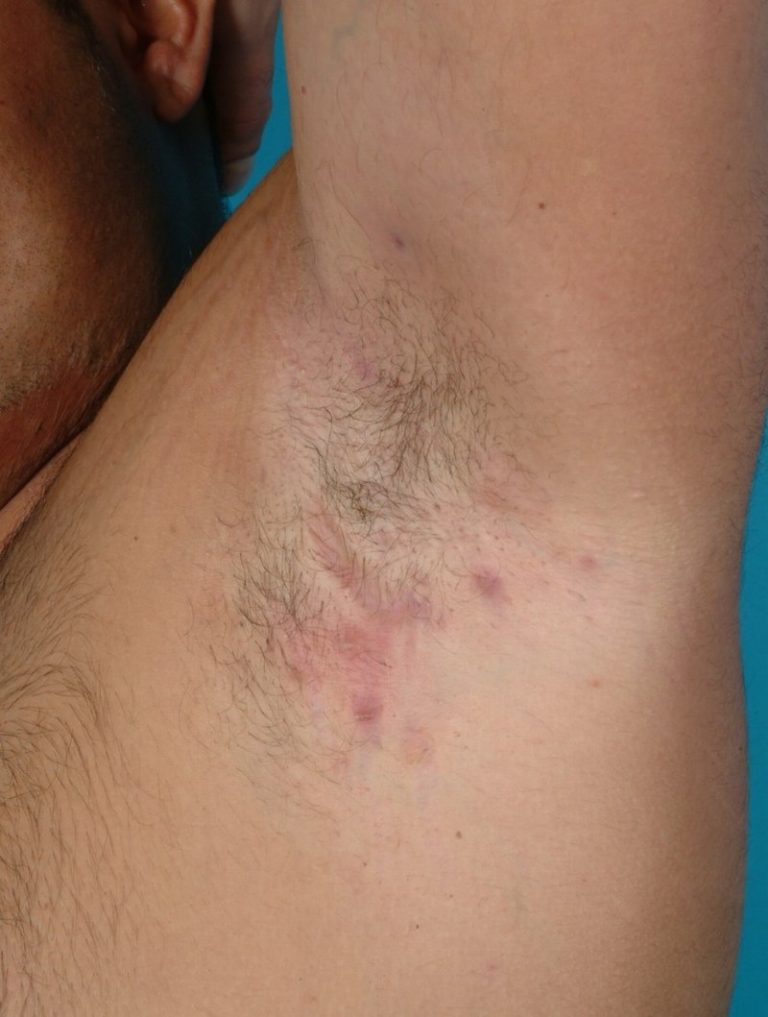
Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a relatively rare condition in Malaysia, and there are no specific statistics on its prevalence in the country. However, it is estimated that the condition affects around 1% of the general population worldwide, and it is more commonly seen in women than men.
HS can be challenging to diagnose and treat, and many individuals may go undiagnosed for years before receiving an accurate diagnosis. In Malaysia, individuals with HS are encouraged to seek medical attention from a dermatologist or other qualified healthcare provider who has experience in treating the condition.